Assignment Tips
Author: Lisa Yan Last updated: September 9, 2023 (Fall 2023)
Jump to:
- DataHub
- JupyterHub Keyboard Shortcuts
- Jupysql: PostgreSQL via ipython magic
- PostgreSQL Client CLI
- PostgreSQL details
- [New] Help! Why is my DataHub so slow?
- Split-screen Setup
- Local Setup
- MongoDB debugging
In most of this course, you will use DataHub to work on projects. PostgreSQL has a few quirks with DataHub that will be covered in this document. However, we strongly encourage you to check out the documentation as you work:
- The official PostgreSQL documentation is great and can even be read cover-to-cover.
- The
jupysqldocumentation is the primary way you will be writing SQL commands for homework submission.
Please see our policies on collaboration before working with any study groups.
DataHub
Working with Jupyter Notebooks
If you are new to using Jupyter Notebooks, please see the first lab assignment of Data 100 (course website). Data 101 assignments work very similarly; there are local and hidden autograder tests, the latter of which are run after you submit your assignment through Gradescope.
Reminder about adding new cells: If you would like to add new cells, always do so before the cell in which you end up writing your answer. Failure to do so may break the auto-grader.
JupyterHub Keyboard Shortcuts
First, to enter shortcut mode/exit editing mode, press Esc. This will then enable you to use any of the below keyboard shortcuts.
| Operation | Keys |
|---|---|
| To enter shortcut mode/exit editing mode | Esc |
| Enter edit mode | Enter |
| Insert cell above | A |
| Insert cell below | B |
| Delete selected cell | D + D (Press D twice) |
| Undo cell operation | Z |
| Copy cell | C |
| Paste cell | V |
| Paste cell above | Shift + V |
| Redo | Ctrl + Shift + Z |
| Undo | Ctrl + Z |
Jupysql: PostgreSQL via ipython magic
What is line/cell magic?
Before getting started, read about line magic (%) and cell magic (%%) here. These commands will be used extensively in this project and future projects to aid us in running SQL queries.
To call SQL commands, we use the Python package jupyql. We strongly recommend you check out the jupysql documentation. It has a lot of hidden gems!
To load jupysql, run:
%load_ext sql
You will often seen this written as the following, which lets you reload the extension multiple times if there is an issue.
%reload_ext sql
Making SQL queries in jupysql
Here are the two ways of writing a SQL query and storing the query result into a Python variable result:
- Single-line magic:
result = %sql SELECT * FROM table ... - Multi-line cell magic:
%%sql result << SELECT * FROM table ...
Opening a database connection
Before running any SQL queries, you must have a working connection to a database on a postgres server. It usually looks something like this, which connects to the local Postgres server and the database imdb.
%sql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb
Closing a database connection
You may sometimes wnat to close the database connection, in case you want to delete your database and start from a new copy. To close the connection, you can either restart your kernel or explicitly run the following in its own cell:
%sql --close postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb
If that’s not working, see the bottom of this page for how to relaunch your DataHub instance.
PostgreSQL Client CLI
The psql program is the PostgreSQL client CLI, or Command-Line Interface. Knowing psql is very useful to understand what your database looks like, execute meta-commands, and explore quick queries.
Open a Terminal in DataHub
To open a Terminal in DataHub, Navigate to Data101’s DataHub, then go to File -> New -> Terminal. Note: Do not open a Terminal on your local machine; it does not know how to connect to DataHub’s server, much less your DataHub’s postgres server!
Opening a database connection
This connects to the imdb database, if it has been created: psql postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/imdb
If no database has been created:
- You will likely get this error:
psql: error: connection to server at '127.0.0.1', port 5432 failed: FATAL: database "imdb" does not exist" - In this case, you can still connect to the server and list databases, etc., as follows:
psql postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432 - However, you won’t be able to see any relations, because this default connection cannot access what’s in
imdb. - To create the
imdbdatabase, see the corresponding Jupyter notebook and run the cells that contain commands such asCREATE DATABASE. For Fall 2023,imdbis created in the Project 1 notebook.
Closing a database connection
\q: This exits out of the psql program and also closes your current connections.
\c <databasename>: This keeps your psql client open, closes your current database conection, and opens a connection to <databasename>.
psql Meta-commands
Postgres meta-commands doc: list
| Meta-Command | Description |
|---|---|
\l | Lists databases |
\d | Lists relations |
\d tablename | List schema of the relation tablename. |
\q | Quit psql |
\? | Help |
Making queries: You can write queries in psql, too! To write queries that span multiple lines, simply use the newline key (i.e., <Return>). However, to execute a query in psql, you must use the semicolon. This is generally good style, anyway!
Display screen: If a query’s result will span more than the available display screen, psql will launch a different display screen. You can navigate this screen by pressing <space> to display more, up/down arrows to scroll up and down, or q to quit.
Terminal commands
Here are some Terminal shortcuts to help you better navigate psql:
| Keys | Description |
|---|---|
| <ctrl>-c | Cancel current operation |
| <ctrl>-a | Jump to beginning of line |
| <ctrl>-e | Jump to end of line |
| <ctrl>-<left> | Jump to previous word |
| <ctrl>-<right> | Jump to next word |
| <space> | If currently exploring a query result, see more of the result. |
| q | If currently exploring a query result, exit from the result. |
PostgreSQL details
DataHub’s local PostgreSQL Server
Instead of connecting to a remote server, we actually connect to a local server. For example, in Project 1, we connect to:
postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb
- connect to
localhostIP (private IP address127.0.0.1on port5432 - connect using JupyterHub username
joyvan(why is the default username? see here Jupyter, JupyterHub) - connect to the database
imdbon this server. Note that if theimdbdatabase has not yet been created, this connection may fail.
Catalog, Schema, Relation/Table, etc.
-
StackOverflow: Catalog, Schema, Relation/Table differences
pg_toast: TOAST storage schema documentation 73.2pg_catalog: System catalog schema documentation 5.9.5
[New] Help! Why is my DataHub so slow?
If you are encountering any of the following issues:
- Your SQL queries are taking a long time to run
- Your SQL queries fail with
No space left on device - Your DataHub is slow or unresponsive
Then, you may have run out of disk or memory space on your DataHub server. Here is a list of things you can do to fix this:
-
Restart your current Jupyter kernel. To do so, go to Kernel -> Restart Kernel and clear outputs of all cells. Then, refresh the page or navigate back to https://data101.datahub.berkeley.edu.
-
Check your display limits. If your row display limit is unbounded, then your notebook will crash. Clear all cell output and insert a cell close to the top of the notebook that sets the display limit to a more reasonable size, like
%config SqlMagic.displaylimit = 50 -
Close all Jupyter kernels other than the one that you are currently working on. To do so, go to the left sidebar and click on the stop button (dark circle with a light inscribed square). Go to Kernels, hover over each item, and hit the X button. Or, click “Shut Down All” with all notebooks still open, then manually start your kernel in the desired notebook.
- Run
VACUUM FULL. This command will instruct PostgreSQL to try to reclaim some space. To do so, run!psql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb -c 'VACUUM FULL'- If your notebook is already unresponsive, you can run this command in a terminal window instead. To do so, go to File -> New -> Terminal. Then, run type
psql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb -c 'VACUUM FULL'(notice that we don’t need to type!in the terminal).
- If your notebook is already unresponsive, you can run this command in a terminal window instead. To do so, go to File -> New -> Terminal. Then, run type
-
Drop and re-create your database. To do so, run the database setup commands in the beginning of your project notebook that includes the
DROP DATABASEandCREATE DATABASEcommands.To find out the size of all current databases, run
- In Jupyter notebook:
!psql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/ -c '\l+' - In a Terminal outside of a psql session:
!psql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/ -c '\l+' - In an active psql session:
\l+
If you are unable to drop the database, it might be because you have other open connections to the database. Run the below to terminate all other connections (replace
imdbwith your database name):- In Jupyter Notebook, make a new cell. Make sure you replace the syntax with the desired database (e.g., below it is
imdb)!psql postgresql://jovyan@127.0.0.1:5432/imdb -c 'SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pg_stat_activity.pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE datname = current_database() AND pid <> pg_backend_pid();' - In
psql, run the following command. Make sure you are conneted to the target database first.- To connect to
imdband delete all otherimdbconnections, use the meta-command\c imdb. - Then, run
SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pg_stat_activity.pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE datname = current_database() AND pid <> pg_backend_pid();
- To connect to
- In Jupyter notebook:
-
Restart your DataHub server. To do so, go to File -> Hub Control Panel -> Stop My Server. Then, refresh the page or navigate back to https://data101.datahub.berkeley.edu.
- If none of the above work, please post on Ed with the following information:
- Your DataHub username (your @berkeley.edu name)
- The project you are working on
- The output of the following commands:
!df -h!free -h!psql -c 'SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_database_size(current_database()))'
Split-screen Setup
Want to splitscreen your JupyterHub? Simply drag a tab over to a different side of your JupyterHub. We recommend splitting your screen with your Jupyter notebook in one window, and a psql terminal in another window, like so (note these are two separate connections to the database!):
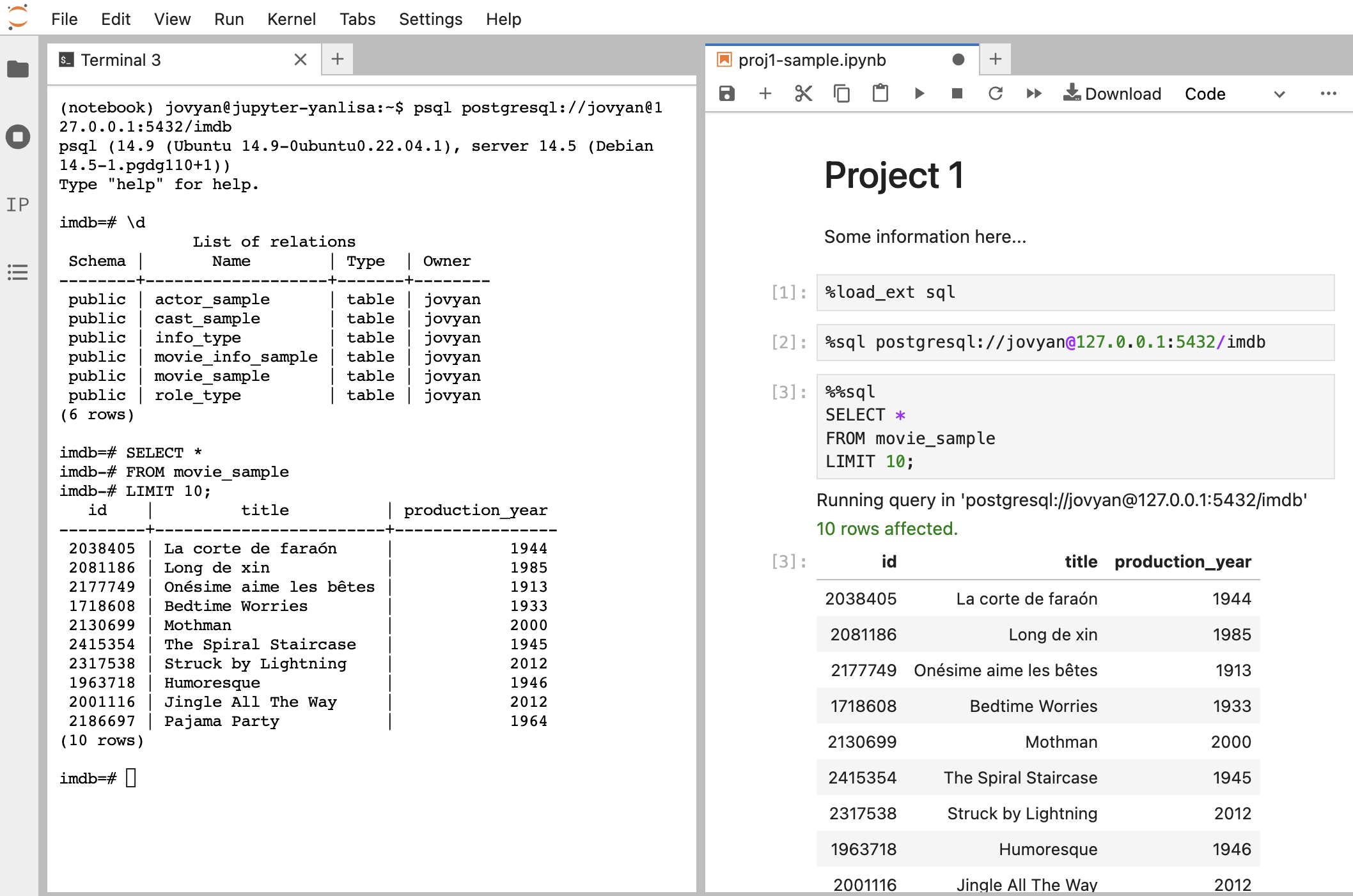
Local Setup
While you are welcome to set up everything locally, when grading we will assume that your submission was developed on DataHub. If you would like to develop locally, please make sure you have the following installed:
otter-grader==5.1.3jupysql==0.10.0pgspecial=1.13.1psycopg2==2.9.6mongodb- PostgreSQL server. For Mac, I use Postgres.app.
Either way, we recommend you always work on DataHub, as staff will not be able to debug/support local setup issues in Fall 2023.
MongoDB debugging
To prevent bracket mismatches while creating your queries, it is recommended to turn on “Auto Close Brackets” via Settings in JupyterHub. Furthermore, since we are using Python dictionaries as our query filter, make sure to wrap all keys and values inside quotes.